AI for Developing Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
As the world grapples with the escalating climate crisis, reducing carbon emissions has become an urgent priority. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies have emerged as a pivotal solution to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, ensuring a sustainable future. Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a transformative role in advancing CCS technologies, enhancing their efficiency, scalability, and integration into global energy systems.
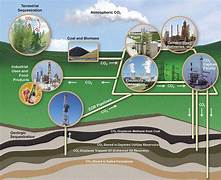
The Importance of Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage is a process that involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from industrial processes or directly from the atmosphere, transporting it, and storing it underground to prevent its release into the atmosphere. CCS is crucial for:
- Reducing Industrial Emissions: Industries such as cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing contribute significantly to global CO2 emissions. CCS enables these sectors to lower their carbon footprint.
- Supporting Net-Zero Goals: Achieving net-zero emissions requires removing residual emissions from hard-to-abate sectors.
- Enhancing Energy Transition: CCS allows continued use of fossil fuels during the transition to renewable energy sources.
Challenges in CCS Implementation
Despite its potential, CCS faces several challenges:
- High Costs: The process of capturing, transporting, and storing CO2 is expensive.
- Energy Intensity: Carbon capture requires substantial energy, which can offset its environmental benefits.
- Storage Risks: Ensuring the long-term stability of stored CO2 remains a concern.
- Limited Deployment: CCS technologies are not yet widely adopted due to technological and regulatory barriers.
AI offers solutions to these challenges by optimizing each stage of the CCS process.
AI Applications in Carbon Capture
1. Enhancing CO2 Capture Efficiency
AI-driven models improve the efficiency of CO2 capture by optimizing chemical processes and materials. Applications include:
- Advanced Material Design: AI algorithms help identify and develop advanced sorbents, membranes, and solvents for capturing CO2 more effectively.
- Process Optimization: Machine learning (ML) models analyze operational data to optimize capture processes, reducing energy consumption and costs.
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI enables real-time monitoring and control of capture systems, ensuring optimal performance under varying conditions.
2. Optimizing Transportation Networks
Transporting captured CO2 to storage sites involves complex logistics. AI aids in:
- Route Optimization: AI-powered tools calculate the most efficient transportation routes, minimizing costs and environmental impact.
- Risk Assessment: Predictive analytics identify potential risks, such as pipeline leaks, ensuring safe transportation.
- Infrastructure Planning: AI assists in designing CO2 transport networks that integrate with existing infrastructure.
3. Improving CO2 Storage and Monitoring
The effectiveness of CCS depends on the secure and permanent storage of CO2. AI contributes to:
- Site Selection: AI analyzes geological data to identify optimal storage sites with high capacity and low leakage risks.
- Leakage Detection: ML models detect anomalies in storage systems, enabling rapid response to potential leaks.
- Long-Term Monitoring: AI systems continuously monitor storage sites, using remote sensing and IoT devices to ensure stability.
AI in Direct Air Capture (DAC)
Direct Air Capture (DAC) involves capturing CO2 directly from the atmosphere. AI enhances DAC by:
- Improving Sorbent Efficiency: AI identifies materials with high CO2 absorption capacity.
- Energy Optimization: ML models reduce the energy requirements of DAC processes, improving cost-effectiveness.
- Deployment Planning: AI supports strategic placement of DAC facilities to maximize capture potential.
Integrating AI with Renewable Energy for CCS
AI enables the integration of CCS with renewable energy systems, addressing energy intensity concerns:
- Dynamic Energy Allocation: AI manages energy supply from renewables to power CCS operations efficiently.
- Hybrid Systems Design: AI designs hybrid systems combining CCS with renewable energy technologies, such as bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS).
- Cost Reduction: AI minimizes operational costs by optimizing energy usage and reducing downtime.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Several organizations and research initiatives demonstrate the potential of AI in CCS:
- CarbonClean Solutions: This company leverages AI to enhance solvent-based carbon capture systems, achieving lower costs and higher efficiency.
- ExxonMobil: AI-powered tools are used to analyze geological data for CO2 storage site selection and monitoring.
- Global CCS Institute: Research initiatives employ AI to develop predictive models for storage site behavior over decades.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI significantly advances CCS, it also introduces challenges:
- Data Availability: High-quality data is essential for training AI models, but environmental data is often limited or fragmented.
- Algorithm Bias: Biased algorithms can lead to inaccurate predictions, affecting CCS outcomes.
- Energy Consumption: Training AI models requires substantial computational resources, which may counteract some environmental benefits.
- Regulatory Compliance: AI applications must comply with evolving regulations governing CCS and environmental technologies.
The Future of AI in CCS
AI will continue to shape the future of CCS through:
- Autonomous Systems: Fully automated CCS systems powered by AI will minimize human intervention and maximize efficiency.
- Integrated Climate Solutions: AI will integrate CCS with other climate mitigation technologies, such as afforestation and renewable energy.
- Policy Development: AI-driven insights will inform policies and investment strategies for scaling CCS globally.
- Public Awareness: AI tools will enhance public understanding of CCS benefits and encourage community engagement.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing carbon capture and storage technologies, addressing key challenges and unlocking new possibilities. By improving capture efficiency, optimizing transportation, ensuring secure storage, and integrating with renewable energy systems, AI accelerates the deployment of CCS as a critical tool in combating climate change. Continued investment in AI research and collaboration among stakeholders will be essential to realize the full potential of CCS and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.